Bones and joints are the pillars of our body, enabling us to move and be active. However, with age or due to certain conditions, these pillars can weaken, leading to uncomfortable and often painful diseases. Our bones and joints are a complex system that requires a balance of different nutrients to function optimally. Magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3 play a key role in maintaining bone and cartilage health, and their deficiency can contribute to the development and worsening of diseases such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout.
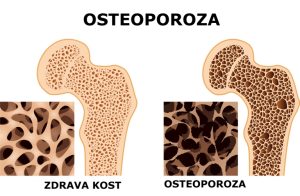
Osteoporosis: The silent bone thief
Osteoporosis is a disease characterized by the loss of bone mass and density, which makes bones fragile and prone to fractures. It is often called a ‘silent thief’ because symptoms usually do not appear until a fracture occurs.
Causes:
- Calcium and vitamin D deficiency
- Hormonal changes (especially in menopausal women)
- Genetic predisposition
- Lack of physical activity
How magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3 deficiency affects osteoporosis:
- Magnesium is essential for the absorption and utilization of calcium, the main building block of bones. It activates enzymes involved in converting vitamin D to its active form, which is crucial for calcium absorption in the intestines. Magnesium deficiency can lead to reduced calcium absorption, which weakens bones and increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Vitamin D3 is essential for calcium absorption in the intestines. It stimulates the production of proteins that bind calcium and allow its transport into the bloodstream. Vitamin D3 deficiency leads to reduced calcium absorption, which weakens bones and increases the risk of osteoporosis.
- Collagen is also important for bone structure, giving them flexibility and resistance to fractures. Collagen deficiency can weaken bones and increase the risk of osteoporosis.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune joint disease
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling. Over time, rheumatoid arthritis can lead to joint damage and deformities.
Causes:
- Autoimmune response
- Genetic predisposition
- Environmental factors
How magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3 deficiency affects rheumatoid arthritis:
- Vitamin D3 has anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
- Magnesium can help control and reduce joint inflammation because it has anti-inflammatory properties. It also participates in the regulation of the immune system, which is important for controlling the autoimmune reactions that cause rheumatoid arthritis.
- Collagen is important for the health of cartilage, which is damaged in rheumatoid arthritis. Vitamin D3 also participates in the regulation of the immune system, which is important for controlling autoimmune reactions in rheumatoid arthritis.

Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis, caused by the wear and tear of cartilage in the joints. This leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced joint mobility.
Causes:
- Aging
- Obesity
- Joint injuries
- Genetic predisposition
How magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3 deficiency affects osteoarthritis:
- Vitamin D3 can help maintain healthy cartilage and joints and reduce pain in osteoarthritis because it has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Magnesium is essential for the proper function of muscles and nerves, which are important for joint support and stability. Magnesium deficiency can lead to muscle weakness and cramps, which can worsen the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Collagen is the main protein in cartilage, the tissue that lines the joints and allows smooth movement. It gives cartilage strength and elasticity, and absorbs shocks during movement. Collagen deficiency leads to weakening of the cartilage, which increases the risk of osteoarthritis.
Gout: Painful crystals in the joints
Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to sudden attacks of severe pain, redness, and swelling.
Causes:
- High uric acid levels in the blood
- A diet rich in purines (red meat, seafood)
- Genetic predisposition
- Overconsumption of alcohol
How magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3 deficiency affects gout:
- Magnesium helps the kidneys excrete uric acid more efficiently, thereby reducing its concentration in the blood. It can also help prevent the crystallization of uric acid in the joints, which is a key factor in gout attacks.
- Gout is characterized by joint inflammation, and vitamin D3 has anti-inflammatory properties. It can help reduce inflammatory cytokines, which are key mediators of inflammation in gout.
- Collagen is crucial for the health of connective tissue, which surrounds and supports the joints. Strengthening connective tissue can help stabilize joints and reduce pain. It can also help restore and maintain cartilage health, thereby reducing pain and stiffness.
Tips for bone and joint health
- A balanced diet and dietary supplements rich in calcium, magnesium, collagen, and vitamin D3.
- Regular physical activity, including strength and stretching exercises.
- Maintaining a healthy body weight
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Regular check-ups with a doctor and monitoring bone and joint health.




